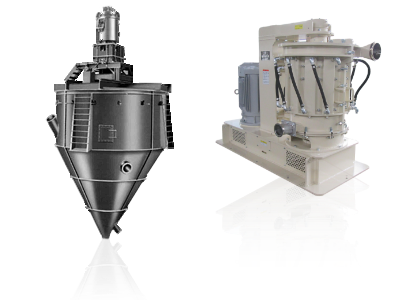
製品情報 PRODUCT

お知らせ INFORMATION

創業100年
以上の実績
ご要望に応じた
機械のご提案

リピーター
のお客様多数
多種多様な
業界への納入実績

海外への納品実績
25カ国以上



創業100年
以上の実績

ご要望に応じた
機械のご提案

リピーター
のお客様多数

多種多様な
業界への納入実績

海外への納品実績
25カ国以上